Bigger is not necessarily better when it comes to the ‘tail’ of a teenager’s brain, researchers at the University of the Sunshine Coast (USC) have found.
A study of 49 local adolescents revealed that when a part of their brain known as the caudate was smaller, it was linked to greater mental wellbeing such as optimism.
The caudate is located towards the centre of the brain and is long and curved and wraps around the sub-cortical parts, which is why it is named after the Latin word for ‘tail’.
The ground-breaking research by USC’s Thompson Institute has been published in Brain Research.
The team assessed 12-year-olds who have signed up for the institute’s Longitudinal Adolescent Brain Study (LABS).
The youngsters undertook a wellbeing questionnaire and their brains were also scanned on MRI to measure different structures.
Lead author Ms Amanda Boyes said the findings could one day help pinpoint teenagers who needed mental health interventions or preventative programs.
“What this means is that bigger is not necessarily better when it comes to the size of the caudate in adolescents,” Ms Boyes said.
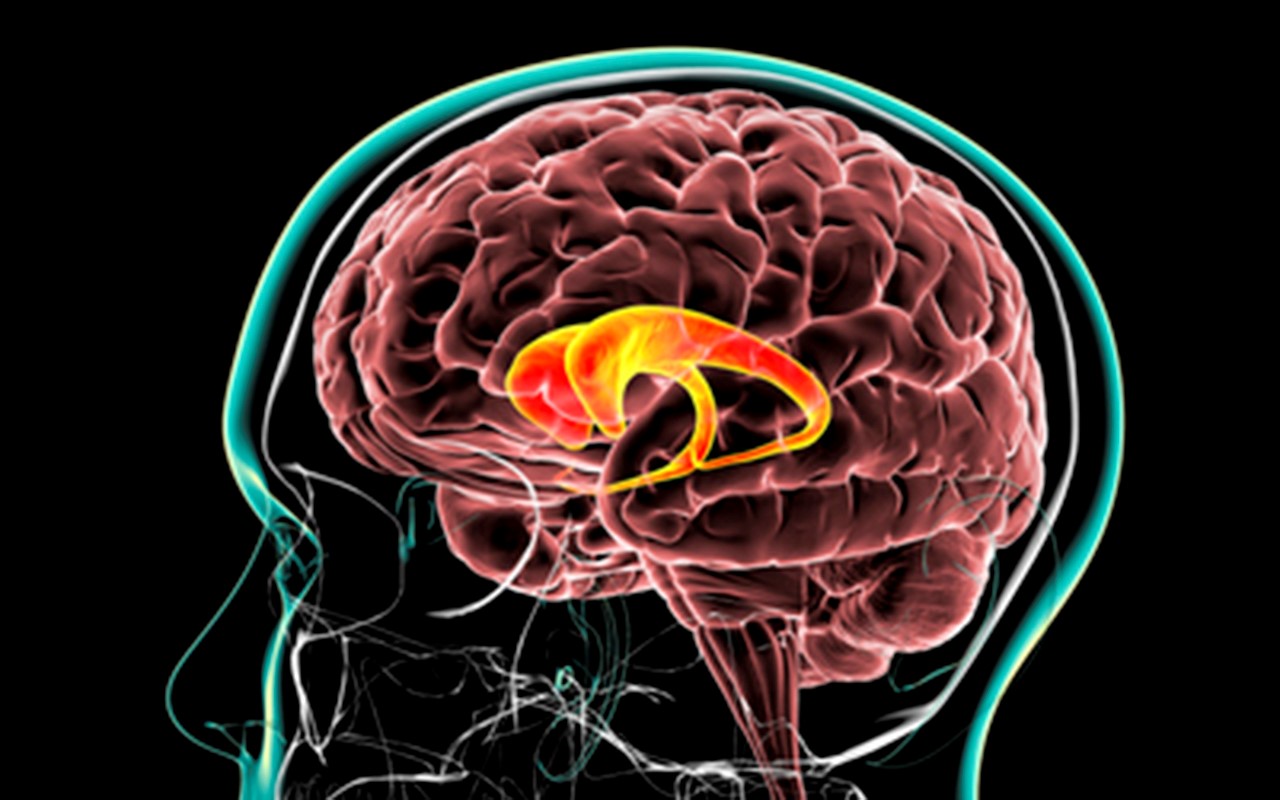
“The caudate links the executive function regions to the emotion processing regions of the brain.
“It has been associated with movement, motivation and reward and there may be something here that differentiates between people reporting higher levels of wellbeing earlier.
“The fact that a smaller caudate is linked to greater wellbeing might mean that this particular area of the brain has become more efficient early on, but we still need to do further research to understand why.”
Study supervisor Professor Daniel Hermens, who leads LABS, said adolescence was a critical time to identify mental health issues, as onset of problems at this stage could last well into adulthood.
“The 12-year-olds coming into our study are at a crucial time in their lives for detection and intervention of mental health problems,” Professor Hermens said.
“And yet despite this, youth mental health is still one of the most under-studied areas of mental health.
“Considering the rising number of cases, it’s vital that we are looking for biomarkers in the brain like this that could inform youth wellbeing programs and interventions.
“If we know more about the unique characteristics of the brain that might be linked to mental health conditions, we might have better responses to the negative impacts, and could reduce the severity of mental health problems long into adulthood.”
Other focuses of LABS include youth anxiety and attention, cyberbullying and COVID impacts on youth levels of worry over time.





